It was late in 2019 when, on a visit to my GP, he asked me if I could bring my son Ken to an appointment in the near future. I was a little uncertain of the reason, but then again doctors, and especially GPs, often have their reasons. Several weeks later, when Ken accompanied me, my GP asked him a rather penetrating question: “Have you noticed anything about your dad’s facial expression?”
It was to be the start of an unexpected journey that has led me to face some hard truths.
Few find it easy to face the reality of ageing. For many years I’ve sought to maintain vigorous exercise, follow a nutritious vegetarian diet and keep my mind healthy and active. So, when my GP referred me to a neurologist for some “Parkinson” symptoms, it confronted me with the reality of degenerative processes in my own life. Though it was difficult, I felt at the time that it was critical and helpful to acknowledge the reality of changes with transparency.
At first, I was not keen to share widely the nature of my diagnosis—Parkinson’s disease or “PD” as it is commonly referred to. Labels can be stigmatising. But, there were some signs that others had noticed.

At church, some had said “Harley seems to have lost his mojo!” Never to my face, but via the grapevine the stories came back.
My neurologist recommended several books for me to read. After purchasing them and digesting their content,1,2,3 I began to understand a little more clearly the nature of symptoms I had been experiencing for some time.
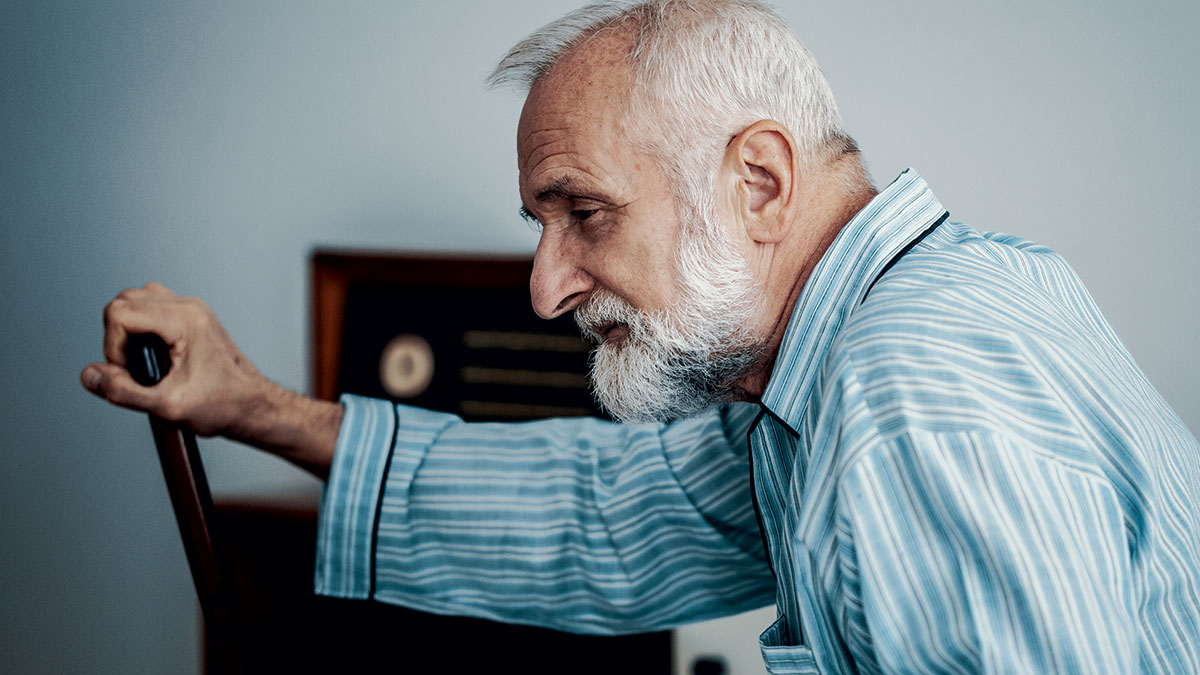
The major features of Parkinson’s are broken down into four plus two: the four—tremors particularly in the hand or face, muscle rigidity or stiffness, slowness or poverty of movement (particularly in short steps), and postural instability or balance difficulties—plus two others: small handwriting (micrographia) and facial masking (hypomimia).
These are or were evident to a greater or lesser extent in my situation. I was particularly aware of the fact that I seemed much more surly in my face and did not smile as much as I’d been accustomed to in my life.
In reading the materials I began to seek answers as to why this might have occurred to me. Could it have been my exposure to pesticides and chemicals on the farm when I was growing up? Was it something genetically determined in my DNA? To what extent can I change and influence the outcome?
The story of Parkinson’s disease begins with an essay or small monograph by James Parkinson in East London in 1817 about a disease he called “the shaking palsy”. A few other physicians at the time started to document similar cases. French physician Jean-Martin Charcot had obtained a copy of Parkinson’s essay and proposed the name “Parkinson’s disease”. Charcot systematically studied the cases he saw and realised the similarity of symptoms. Some years later, in 1919, a Russian student by the name of Konstantin Tretiakoff showed convincingly that the dissected brains of Parkinson’s patients had lost black stuff from the substantia nigra area of the brain. He discovered the hallmark of the patient with Parkinson’s disease to be the existence of what he named “Lewy bodies”.4 [pullquote]
Over time it became clear that not only had the black stuff vanished, but a brain chemical known as dopamine had also disappeared. It was later shown to be the reason why the critical element of dopamine in orchestrating movement was deficient in Parkinson’s patient’s brains. Dopamine is a chemical produced by our brains that plays a key role in motivating behaviour. It is released when we eat delicious food, when we have intimacy, when we exercise, and, importantly, when we have successful social interactions.
Today most patients are placed on L-dopa medication that aims to replace the loss of dopamine.5 One researcher documented the change in patients in 1968, in a film showing one previously frozen patient taking a stick of chalk and walking to a blackboard and fluently writing out the words “This is a lovely day.” Medication restored a frozen man to an almost normal state!
One outcome of medication is that some people experience an initial benefit, but after some time the L-dopa becomes less effective and they experience more negative symptoms including involuntary movement of the arms, legs or head. For some it is a Faustian bargain: You trade a better “now” for a worse “later”.
A great deal of research is taking place because of the large number of people with PD. It is estimated that approximately four people per 1000 in Australia have Parkinson’s disease, with the incidence increasing to one in 100 over the age of 60. In Australia, there are approximately 80,000 people living with Parkinson’s disease, with 20 per cent, or one in five, of these people being diagnosed before the age of 50.6
Researchers at the Bionics Institute (Vic) are developing a Bionics Institute Rigidity Device (BiRD) designed to monitor the four main symptoms that define Parkinson’s disease: hand tremor, slowness, muscle rigidity (stiffness) and poor balance. The Michael J Fox Foundation in the US is aggressively researching new treatments.
Over the months that followed I came to terms with my diagnosis and have sought to be transparent in the reality of my future. Jon Palfreyman in his book wrote, “I realised that while I was announcing myself to the group that I was conceding something profound: that the diagnosis marked an irreversible change in my identity, the moment that one version of me ended and another version began.”7
As part of the process I wrote to family members and made them aware of my recent diagnosis. They continue to be affirming and supportive. Most people are probably more observant of us than we know. It has been helpful to connect with several others who have been on this journey. When struggling with some of the exercises at the gym some months after my diagnosis, I indicated my situation to some of those present and they were most accepting.
As a result of my understanding of the symptoms I’ve deliberately sought to compensate for some of the reduced smiles, increased the length of my steps, implemented enhanced stretching and taken to the recommended “ta-daas” that are part of using your voice in a more explosive way. These steps aim to offset or compensate for the muscular contraction which accompanies PD.
I participated in a virtual PD Warriors Conference in April that was attended by 8000 participants from across Australia. The conference provided great insights into understanding the disease and what can be done to offset the encroachment of symptoms. It is now clear that exercise that stretches and challenges both brain and body movement is of great benefit in offsetting the progression of the disease in many patients. I attend a PD Warriors class weekly that aims to use exercise and brain coordination to retrain the loss of function. There is also some evidence that keto-based diets appear to give some benefit as well.
I don’t expect that the future will be all smooth sailing. I give thanks to the Lord for the great joys I have experienced in my life and am thankful for each and every day.
A good friend who has been living with PD for more than a decade said to me, “It’s not likely to kill you, but you will die with it!” Another has said, “Don’t let your disease define you.” I agree with both of these!
So, today “In everything, give thanks; for this is the will of God in Christ Jesus for you!” (1 Thesselonians 5:18).
Harley Stanton is a retired eclectic pastor and doctor who worked passionately to reduce tobacco smoking in the Pacific and Asia and now lives in Launceston, Tasmania.